Unlocking the Past: The History of Autism Revealed
Introduction
Autism, with its neurological traits, has existed throughout history, evolving in its understanding. Diagnosing it remains challenging due to cultural, gender, and social factors. The term “autism” was coined by Eugen Bleuler, popularized by Leo Kanner‘s 1943 study. The DSM now recognizes it as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), replacing individual entries like Asperger’s Syndrome. Notably, the self-advocacy movement has emerged, offering firsthand insights from neurodivergent individuals. The focus of autism support is on enhancing quality of life. It is considered a neurodevelopmental condition without a cure.
Ancient Perceptions of Autism

In the past, people didn’t know much about how the brain and development worked. There was no specific term for autism, and actions associated with it were explained according to the beliefs prevailing at that time.
History of autism in Greece
In Ancient Greece, they didn’t talk directly about differences in how people’s brains worked. But from what we know in history, some people who acted in unusual ways might have been seen as a bit strange or having special qualities. Back then, the Greeks mainly valued physical strength and smart thinking. They didn’t fully understand the differences in how brains functioned.
History of autism in India
In India, where people followed spiritual and philosophical traditions. If someone exhibited different behavior, it might have been attributed to spiritual or karmic reasons. Acceptance within the community could vary for those who behaved uniquely. Otherwise, kept away based on what others believed about the reasons for their differences.
History of Autism in United States
In the early 1900s, a psychiatrist named Leo Kanner in the United States first identified autism. Since then, how we understand and recognize autism has changed. Advocacy efforts have led to the creation of laws like IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) to raise awareness about autism and provide support. Research has helped us learn more, and there are now helpful treatments like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA).
Treatment Approaches in Ancient Times
The treatment of individuals exhibiting atypical behaviors in ancient times varied based on cultural, religious, and societal norms.
Spiritual and Ritualistic Approaches
In ancient times, like in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and India, when people acted differently. They believed it might be because of spiritual or supernatural reasons. To fix this, they would use special ceremonies, spiritual activities, or religious rituals to try to bring things back into balance or ask for help from the divine.
Community Integration or Exclusion
The approach towards individuals with atypical behaviors varied widely. Some ancient societies might have integrated such individuals into their communities, while others, influenced by fear or misunderstanding, may have excluded them. The acceptance or rejection often depended on the perceived impact of the individual’s behavior on the community.
Herbal and Natural Remedies
In the past, people often used herbs and natural treatments for different health issues. While not specifically intended for autism, people commonly employ these remedies to address a range of behavioral and health issues. How well these treatments worked depended on what people knew about medicinal plants and the health beliefs of their culture.
Challenges and Support in Ancient Societies
Navigating life as an individual with atypical behaviors in ancient times presented unique challenges and opportunities. The level of societal support or hindrance depended on cultural, religious, and societal attitudes.
Potential for Recognition of Unique Abilities
Sometimes, when people acted differently in the past. They might have been noticed for having special skills that were helpful to their community. Some ancient societies liked having different kinds of people and could give them jobs based on what they were good at. They valued having a mix of abilities and talents in their group.
Stigmatization and Isolation
On the other hand, if people lacked understanding or held misconceptions about differences in how brains work, those who acted differently might have experienced unfair treatment. Others could have excluded or isolated them, creating difficulties in their efforts to become part of the group or gain acceptance.
Role of Families and Community Support
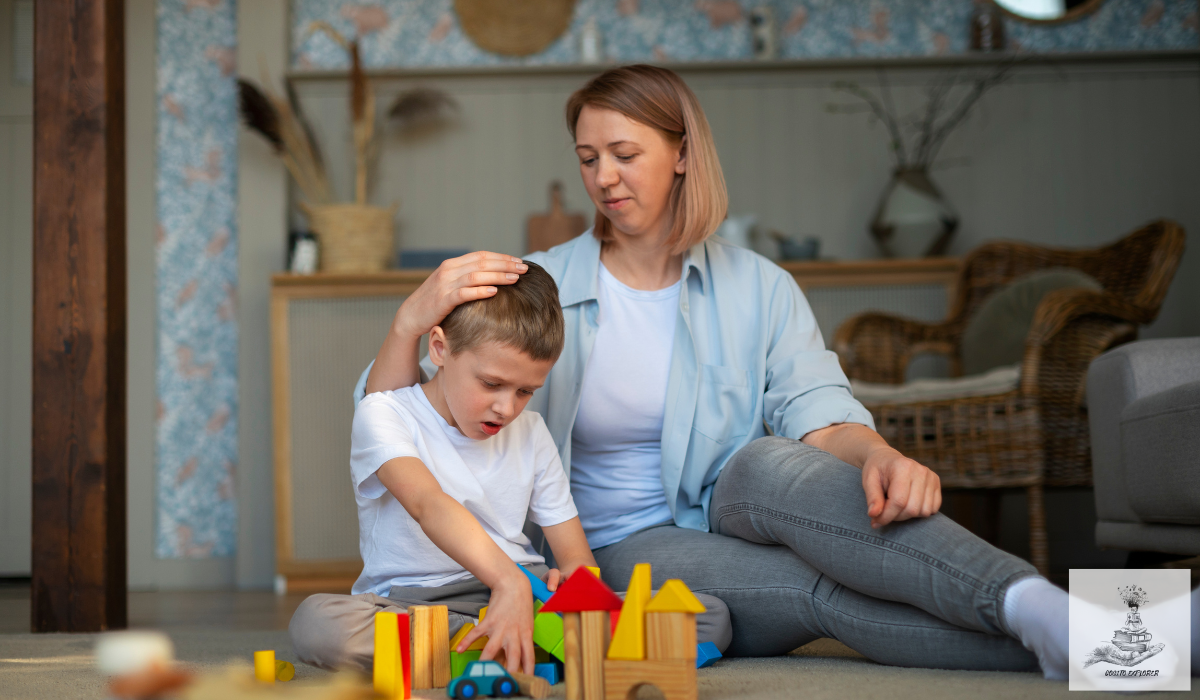

Families and communities played a crucial role in how people with different behaviors were treated. If families and communities were helpful and understanding, they could protect individuals and include them. But when there wasn’t enough support, it could make the challenges for these individuals even harder.
Conclusion
As we’ve learned more about autism over the years. Looking at how people with autism were treated in ancient times. It gives us a detailed view of the history of neurodiversity. Different ancient societies, shaped by their culture, religion, and philosophy, handled individuals with unique behaviors in various ways. Thinking about the past helps us see the improvements we’ve made in understanding and supporting neurodiversity. It’s important to keep promoting inclusivity and acceptance in today’s society.
FAQ’s
Q. Are autistic people retarded?
A. No, autism and intellectual disability are distinct conditions. Many autistic individuals have average or above-average intelligence, and it’s important to avoid outdated and stigmatizing language like “retarded.”
Q. Down syndrome in medieval times?
A. People with Down syndrome likely existed in medieval times. Embracing inclusivity, we recognize the diversity of individuals throughout history.
Q. Ancient Greek term for autism?
A. The ancient Greek term for autism is “autos,” meaning “self,” but it does not directly correlate with the modern concept of autism. The historical understanding of neurodevelopmental conditions differs from contemporary perspectives.
Q. How can I find the best autism therapy provider?
A. Finding the best autism therapy provider involves researching local resources, seeking recommendations from healthcare professionals, and considering the provider’s experience and expertise in working with children on the autism spectrum. Consultation with specialists can help guide the selection process.
Q. What is child autism therapy?
A. Child autism therapy refers to specialized interventions aimed at addressing the developmental challenges faced by children on the autism spectrum. Designed to enhance communication skills, social interactions, and overall well-being, these therapies aim to provide comprehensive support.
Q. How effective is therapy for autism?
A. Therapy for autism has demonstrated effectiveness in enhancing various aspects of a child’s life, including communication and social skills. Early intervention is particularly crucial, and consistent therapy can lead to significant progress over time.